-
Mobile phone: 13724352725
-

Email: liliangbin@szsyjm.com
-

Phone: 0755-22715304
It is an ideal choice for industries such as bearing, tool, woodworking, and automobile manufacturing.
Compared with asynchronous electric spindles and mechanical spindles, synchronous electric spindles have four advantages:
1. Synchronous electric spindle can improve the machining accuracy of the workpiece surface.
2. Synchronous electric spindles can save investment costs for enterprises.
3. Synchronous electric spindle can expand the application range of low-speed powerful cutting and high-speed precision cutting of machine tools.
4. Synchronous electric spindle can save 15% energy for machine tools.
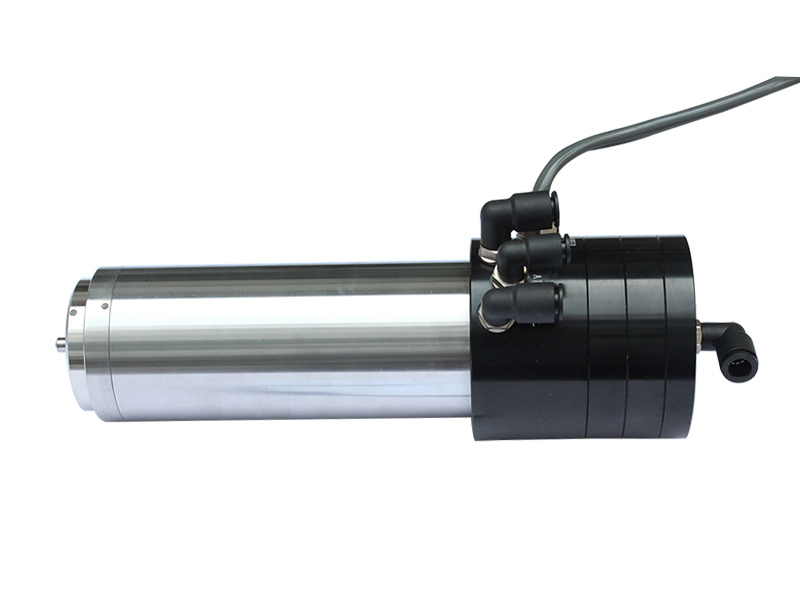

The characteristics of synchronous electric spindle and its differences from asynchronous electric spindle:
1. There is a large induced current in the rotor cage of asynchronous motors, which can cause significant copper loss and heat generation. The temperature of the rotor and spindle can reach around 200 degrees. The spindle undergoes significant thermal deformation and poor axial stability, resulting in low surface machining accuracy; The synchronous motor rotor has no induced current, low rotor heating, and good axial stability of the main shaft, so the surface machining accuracy is high. Synchronous electric spindles have excellent hard torque characteristics, high speed stability under load fluctuations, and can ensure uniform rotation of cutting tools or grinding wheels, resulting in high surface quality of machined parts.
2. In order to meet the power requirements, the rated speed of high-speed electric spindles is generally higher, resulting in a lower rated torque. Therefore, in a larger low-speed range, the load-bearing capacity is poor. If a lower rated speed is selected at the same power, a larger rated torque output is required, and the motor volume will greatly increase. The synchronous electric spindle strictly follows the lateral torque law below the rated speed, and under the same conditions, its volume is reduced by 30% compared to asynchronous motors.
3. Synchronous motors do not require excitation current, with a power factor close to 1, and almost entirely utilize stator current to output torque, resulting in high work efficiency; However, asynchronous motors require a larger excitation current component, resulting in increased motor losses and reduced efficiency. The general power factor is 0.3~0.85. Synchronous motors can save at least 15% energy. In special circumstances, the energy-saving ratio is higher.
4. The rotor surface of a synchronous motor is coated with magnetic steel, which forms a rotor magnetic field directly without excitation; The rotor of asynchronous motors is generally a copper bar or cast aluminum squirrel cage structure, which requires a stator.
E-mail:liliangbin@szsyjm.com
Address:A2 Building,Second row,Baishixia west area,Fuyong Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen